
What you should know about descent-control devices. Safe practices: adjustable-suspension scaffolds. If you erect or dismantle scaffolds, you must have additional training by a competent person that covers scaffold hazards, erecting and dismantling procedures, design criteria, and load capacities. Training for scaffold erectors and dismantlers.
Two point suspended scaffold how to#
How to protect those below the scaffold from falling objects.When fall protection is required, the appropriate protection to use, and how to use it.
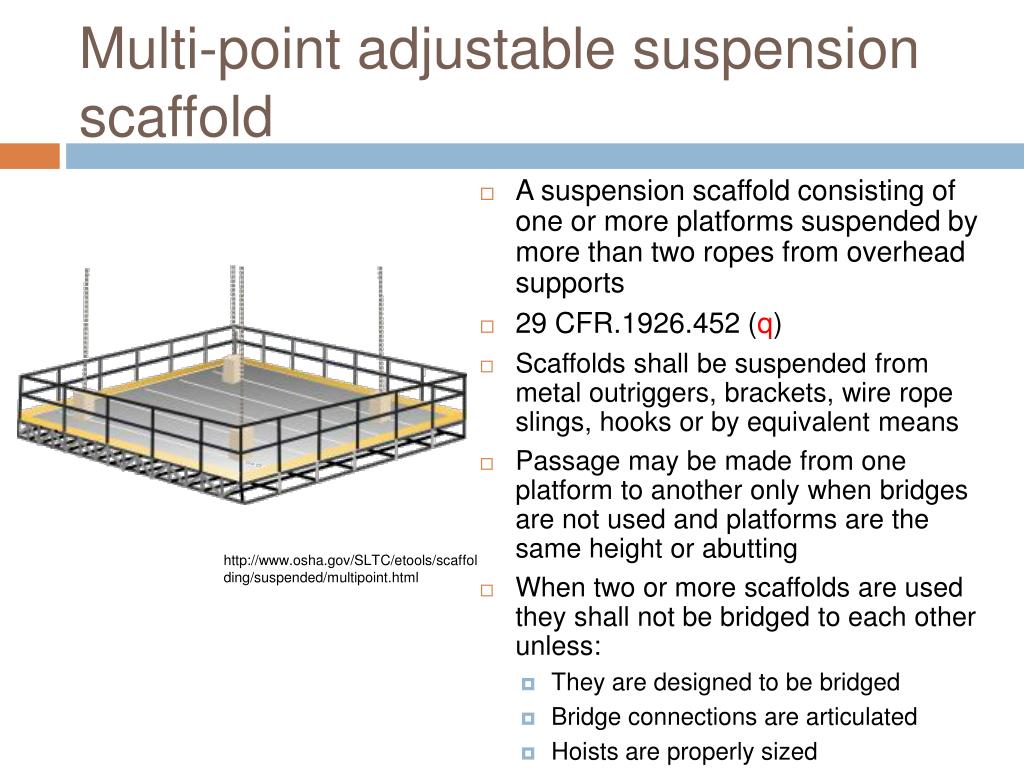
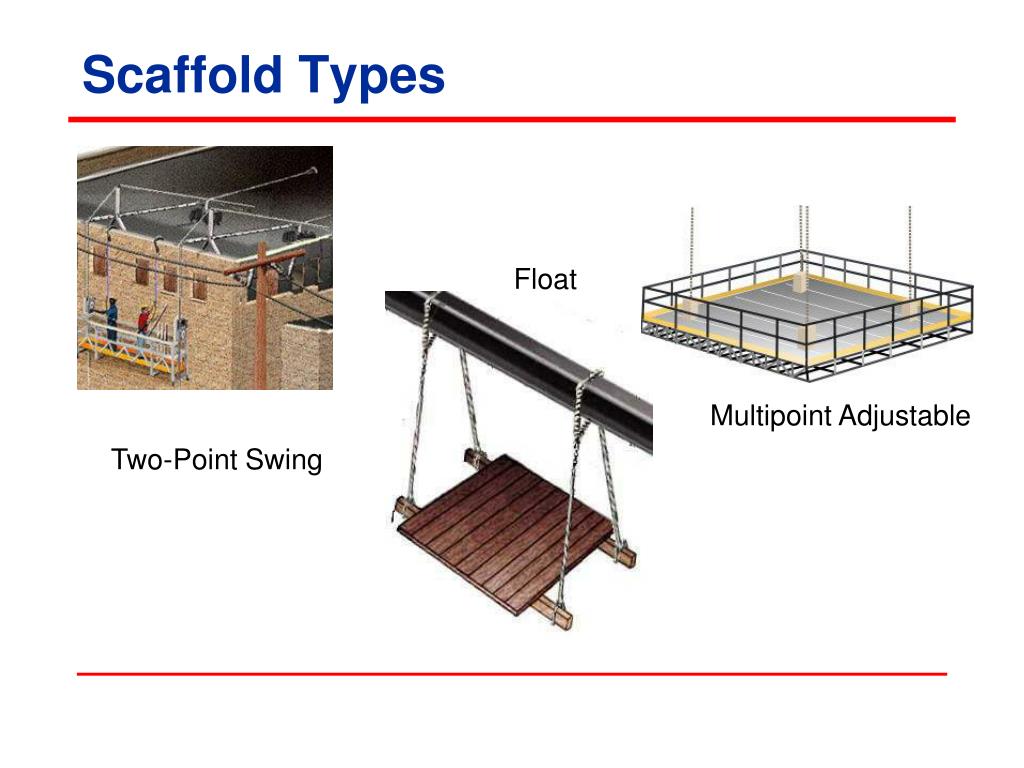 Scaffold load capacity and the types of loads appropriate for the scaffold. Training must cover the following topics: Those who work from adjustable-suspension scaffolds must be trained to recognize fall hazards and toĬontrol or minimize the hazards. (The top edge can exceed 45 inches, when necessary.) Required training. The top edge of the guardrail must be between 36 inches and 45 inches above the platform surface. Multipoint adjustable-suspension scaffolds: Personal fall-arrest systems and guardrail systems are required on multipoint adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Boatswain’s chairs: Personal fall-arrest systems are required for workers who use boatswain’s chairs. (The top edge can exceed 45 inches when necessary.) The top edge of guardrail must be between 36 inches and 45 inches above the platform surface. Single-point and two-point adjustable-suspension scaffolds: Personal fall-arrest systems and guardrail systems are required on single-point or two-point adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Lower level, you must be protected from falling with an appropriate fall protection system. If you work on an adjustable-suspension scaffold more than 10 feet above a When fall protection systems are required. Not sure, have a qualified person determine whether it is safe to use an adjustable-suspension scaffold on these buildings. However, olderīuildings, buildings with large cornices, and tiered buildings often lack adequate support for suspended platforms. Newer buildings and renovated buildings usually have some form of support system for suspension scaffolds. You must also wear a personal fall-arrest system to protect yourself if a connection fails. Work safely from the scaffold, and what to do in an emergency.Ī competent person must examine all direct connections that are part of the system and confirm that the connections will Before you use an adjustable-suspension scaffold, you need to know theĮngineering principles for anchoring and suspending the scaffold, how to rig the scaffold, how to operate the hoist, how to Lifelines can fail when workers hang them over unpadded edges, don’t inspect them, or use ropes not designed for personal These anchors fail because they are not designed to support suspended loads. Too often, untrained workers attach lifelines and suspension ropes to “secure looking” rooftop fixtures for convenience. Pressure from the two steel discs that clamp to the support rope in sheave-type hoistįailing anchors also cause serious accidents. If an ascending platform snags, an electric hoist that continues to When the ropes aren’t maintained, they weaken. Steel suspension ropes rarely break if they are correctly rigged, maintained, and inspected Workers can die during such events if they don’t use personal fall-arrest systems Most accidents involving adjustable-suspension scaffolds happen How falls occur from adjustable-suspension scaffolds. They are often used for chimney cleaning and are called chimney hoists. As the name suggests, these scaffolds are suspended by more than two Multipoint adjustable-suspension scaffolds. They’re used by window cleaners on skyscrapers and by construction workers on high-rise projects. Also known as swing-stage scaffolds, these scaffolds are suspended by two independent ropes from an overhead support device such as a davit or outrigger beam. Two-point adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Most chairs are equipped with descent-control devices. The chair is lightweight, easy to rig, and favored by window cleaners. The platform is usually ground rigged.Ī boatswain’s chair, the most common single-point suspension scaffold, supports only one worker in a sitting position. A single-point suspension scaffold is suspended by a single wire rope from an overhead support device such as a davit or outrigger beam. Basic types of adjustable-suspension scaffolds: Suspension ropes, lifelines, platforms, hoists, overhead support devices, and tieback systems are critical to the safety of adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Add a hoist to move the platform up or down, and you have an adjustable-suspension scaffold, but not necessarily a safe one. A suspension scaffold is a temporary elevated platform that hangs by wire rope.
Scaffold load capacity and the types of loads appropriate for the scaffold. Training must cover the following topics: Those who work from adjustable-suspension scaffolds must be trained to recognize fall hazards and toĬontrol or minimize the hazards. (The top edge can exceed 45 inches, when necessary.) Required training. The top edge of the guardrail must be between 36 inches and 45 inches above the platform surface. Multipoint adjustable-suspension scaffolds: Personal fall-arrest systems and guardrail systems are required on multipoint adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Boatswain’s chairs: Personal fall-arrest systems are required for workers who use boatswain’s chairs. (The top edge can exceed 45 inches when necessary.) The top edge of guardrail must be between 36 inches and 45 inches above the platform surface. Single-point and two-point adjustable-suspension scaffolds: Personal fall-arrest systems and guardrail systems are required on single-point or two-point adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Lower level, you must be protected from falling with an appropriate fall protection system. If you work on an adjustable-suspension scaffold more than 10 feet above a When fall protection systems are required. Not sure, have a qualified person determine whether it is safe to use an adjustable-suspension scaffold on these buildings. However, olderīuildings, buildings with large cornices, and tiered buildings often lack adequate support for suspended platforms. Newer buildings and renovated buildings usually have some form of support system for suspension scaffolds. You must also wear a personal fall-arrest system to protect yourself if a connection fails. Work safely from the scaffold, and what to do in an emergency.Ī competent person must examine all direct connections that are part of the system and confirm that the connections will Before you use an adjustable-suspension scaffold, you need to know theĮngineering principles for anchoring and suspending the scaffold, how to rig the scaffold, how to operate the hoist, how to Lifelines can fail when workers hang them over unpadded edges, don’t inspect them, or use ropes not designed for personal These anchors fail because they are not designed to support suspended loads. Too often, untrained workers attach lifelines and suspension ropes to “secure looking” rooftop fixtures for convenience. Pressure from the two steel discs that clamp to the support rope in sheave-type hoistįailing anchors also cause serious accidents. If an ascending platform snags, an electric hoist that continues to When the ropes aren’t maintained, they weaken. Steel suspension ropes rarely break if they are correctly rigged, maintained, and inspected Workers can die during such events if they don’t use personal fall-arrest systems Most accidents involving adjustable-suspension scaffolds happen How falls occur from adjustable-suspension scaffolds. They are often used for chimney cleaning and are called chimney hoists. As the name suggests, these scaffolds are suspended by more than two Multipoint adjustable-suspension scaffolds. They’re used by window cleaners on skyscrapers and by construction workers on high-rise projects. Also known as swing-stage scaffolds, these scaffolds are suspended by two independent ropes from an overhead support device such as a davit or outrigger beam. Two-point adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Most chairs are equipped with descent-control devices. The chair is lightweight, easy to rig, and favored by window cleaners. The platform is usually ground rigged.Ī boatswain’s chair, the most common single-point suspension scaffold, supports only one worker in a sitting position. A single-point suspension scaffold is suspended by a single wire rope from an overhead support device such as a davit or outrigger beam. Basic types of adjustable-suspension scaffolds: Suspension ropes, lifelines, platforms, hoists, overhead support devices, and tieback systems are critical to the safety of adjustable-suspension scaffolds. Add a hoist to move the platform up or down, and you have an adjustable-suspension scaffold, but not necessarily a safe one. A suspension scaffold is a temporary elevated platform that hangs by wire rope.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
